IT/알고리즘 공부( Coursera )
5week] Balanced Search Trees
Bell_bear
2021. 4. 2. 00:05
반응형
2-3 Search Trees
균형 탐색트리로 자식노드를 2, 3개를 가지고 있는 형태를 가진다.
- 2-node : 1개의 key, 2개의 자식노드
- 3-node : 2개의 key, 3개의 자식노드
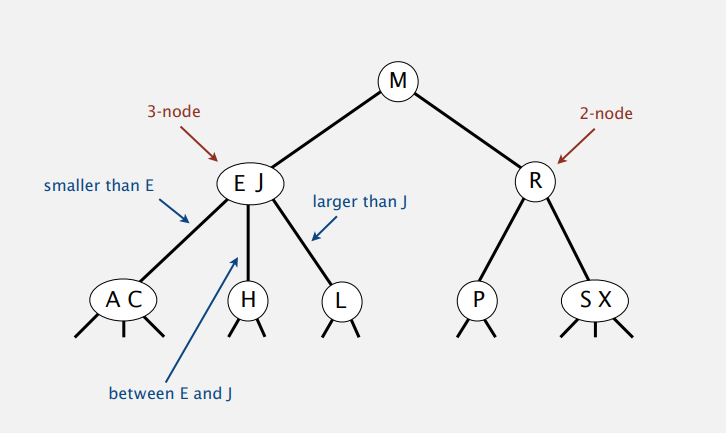
예제에서 보듯 기본 BST와 같이 정렬되어 트리를 구성한다.
특징 : root→leaf(null link)까지의 거리가 모두 같아 완벽한 균형을 이룬다.
Search
- 2-node
- key보다 작으면 → left 자식
- key보다 크면 → right 자식
- 3-node
- 두 key보다 작으면 → left 자식
- 두 key의 사이면 → middle 자식
- 두 key보다 크면 → right 자식
Insert
- 삽입할 target node가 2-node일 때
- 3-node로 교체
- 삽입할 target node가 3-node일 때
- 임의의 4-node 로 교체 ( key가 3개 ) → 이 때 잠시 2-3 Search Tree가 성립하지 않는다.
- 4-node의 key 값의 중간 값을 부모 노드에 추가하고 자식노드를 2-node로 교체 ( 재귀적으로 )
- root 임시로 4-node가 된다면, 1-2)를 거치며 전체의 length가 1 증가한다.
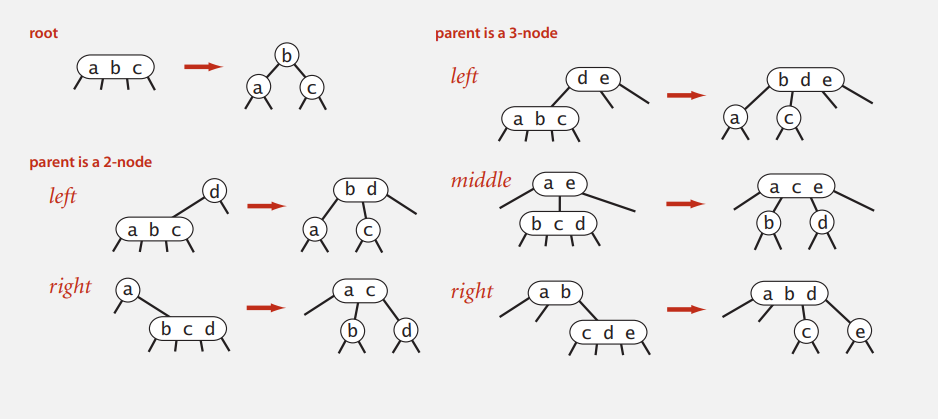
insert가 되는 다양한 예시 그림
2-3 Tree 구현은 따로 안하고, R-B Tree에서 구현을 한다. ( 기존 BST 에서 몇 줄만 추가되는 정도 )
Left-leaning Red-Black BSTs ( R-B Tree )
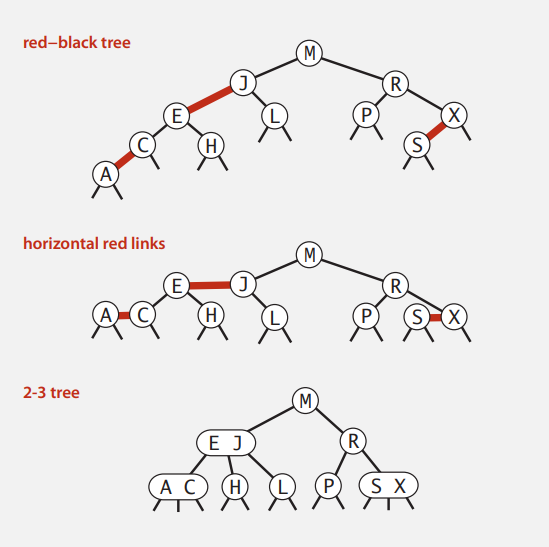
위에서 배운 2-3 Tree를 BST로 나타낸다 . ( 색깔을 나르게 나타내는 방법 사용 )
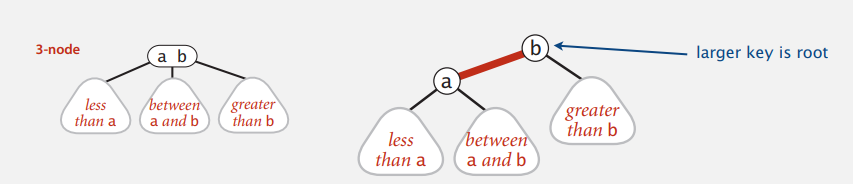
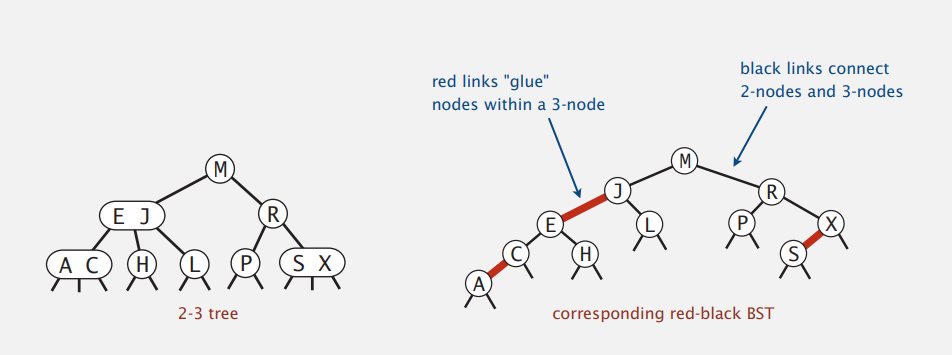
R-B Tree의 규칙
- Red 가 겹쳐지는 노드는 존재하지 않음.
- Red Node는 왼쪽으로 기울어짐
- Root→Leaf 까지 Black Node의 개수가 모두 같음 ( 완벽한 균형 )
2-3 Tree 와 R-B Tree의 1:1 mapping
기존 BST의 연산은 그대로 사용 가능하다. ( search, floor, iteration, selection )
public Val get(Key key)
{
Node x = root;
while (x != null)
{
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0) x = x.left;
else if (cmp > 0) x = x.right;
else if (cmp == 0) return x.val;
}
return null;
}
구현 코드에 color 관련 내용이 없음.
초기화 코드의 경우 color의 내용이 추가된다.
private static final boolean RED = true;
private static final boolean BLACK = false;
private class Node
{
Key key;
Value val;
Node left, right;
boolean color; // color of parent link
}
private boolean isRed(Node x)
{
if (x == null) return false;
return x.color == RED;
}R-B Tree의 경우 총 3가지의 추가되는 기본 연산 3가지가 존재한다.
- left-rotation
- right-rotation
- color-flip
Left-rotation
- 오른쪽으로 치우친 Red link를 왼쪽으로 바꿔주는 연산( 조건 : 왼쪽 자식은 Black이고, 오른쪽 자식이 Red 일 때 )
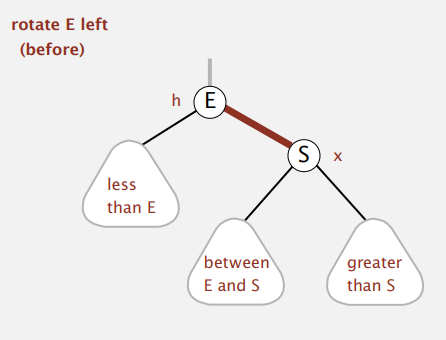
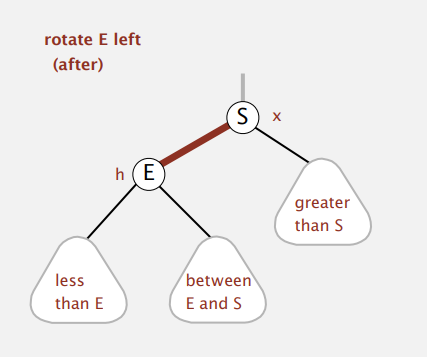
private Node rotateLeft(Node h)
{
assert isRed(h.right);
Node x = h.right;
h.right = x.left;
x.left = h;
x.color = h.color;
h.color = RED;
return x;
}Right-rotation
- 왼쪽으로 치우친 Red link를 오른쪽으로 바꿔주는 연산( 왼쪽의 자식 & 왼쪽 자식의 왼쪽 자식이 Red 일 때 )
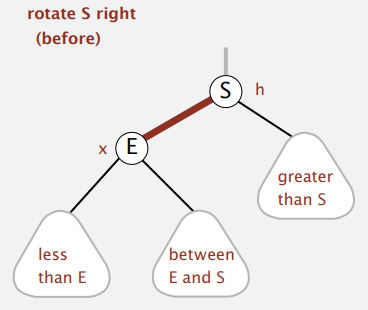
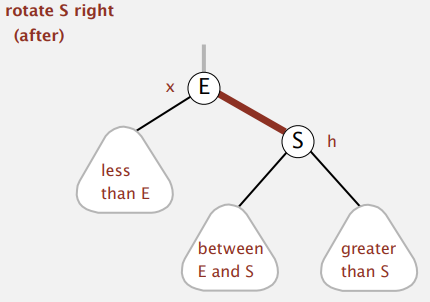
private Node rotateRight(Node h)
{
assert isRed(h.left);
Node x = h.left;
h.left = x.right;
x.right = h;
x.color = h.color;
h.color = RED;
return x;
}Color-filp
- 임시로 4-node가 되었을 때 색을 바꿔주는 연산( 자신은 Black이고 모든 자식이 Red 일 때 )
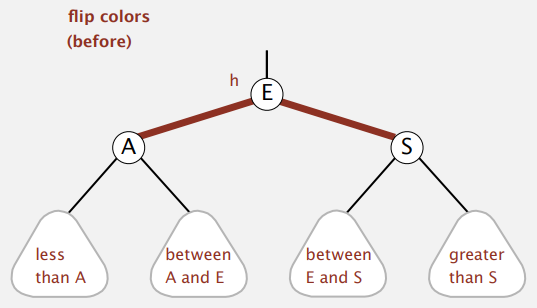
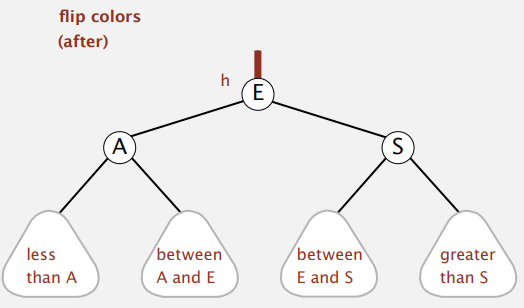
private void flipColors(Node h)
{
assert !isRed(h);
assert isRed(h.left);
assert isRed(h.right);
h.color = RED;
h.left.color = BLACK;
h.right.color = BLACK;
}위의 3가지 연산을 통해 R-B Tree가 유지 되며 기본 전략은 위의 설명과 같이
2-3 Tree 와 1:1 mapping하는 전략
Case 1 : 2-node 에 삽입 ( 자식에 Red Node가 없는 경우 )
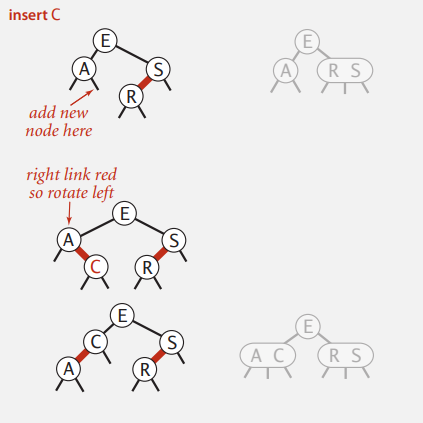
Case 2: 3-node 에 삽입 ( 이미 자식에 Red Node가 있는 경우 )
Case 2-1 : 반복할 필요 없는 경우
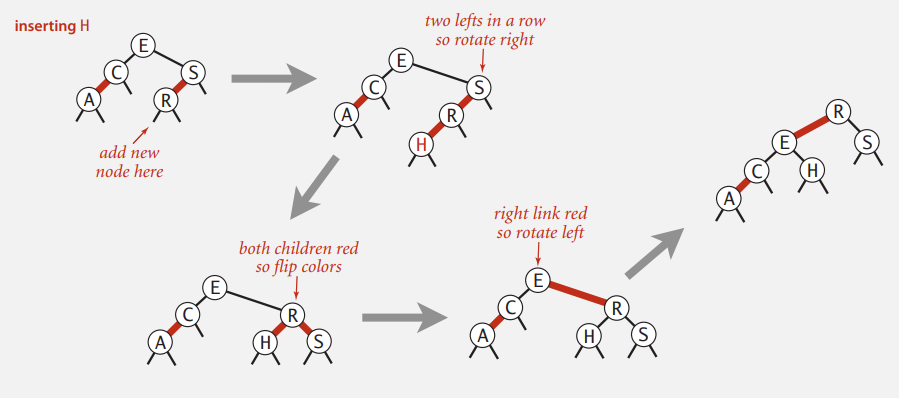
Case 2-2: 반복이 필요한 경우
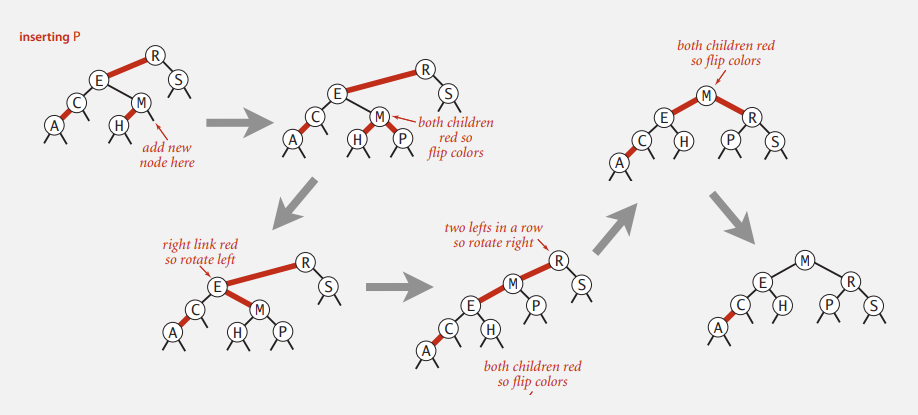
이 모든 Case 를 같은 코드에서 처리하도록 만들어야함. ( insert )
private Node put(Node h, Key key, Value val)
{
if (h == null) return new Node(key, val, RED);
int cmp = key.compareTo(h.key);
if (cmp < 0) h.left = put(h.left, key, val);
else if (cmp > 0) h.right = put(h.right, key, val);
else if (cmp == 0) h.val = val;
if (isRed(h.right) && !isRed(h.left)) h = rotateLeft(h);
if (isRed(h.left) && isRed(h.left.left)) h = rotateRight(h);
if (isRed(h.left) && isRed(h.right)) flipColors(h);
return h;
}R-B Tree는 균형있는 Tree가 만들어지며, 검색 속도가 안정적

반응형